 |
Variational quantum Monte Carlo ground state of GaAs |
![]()
|
A highly accurate many-partice calculation for the GaAs bulk
is applied to provide several properties of the semiconductor like the
lattice constant, bulk modulus, charge transfer of
the bonding, or correlation energy. These results demonstrate
the progress which has been made with many-partice solutions of the
Schrödinger equation in solid state physics. The variational quantum Monte Carlo method is an attractive technique for many-particle calculations, because the quality of the result is controlled by a simple rule: the lower the energy the better the wave function. Additionally, the statistical error of an expectation value can be safely estimated. Thus this method is really ab initio, not relying on any uncontrolled quantity, such as an unknown correlation function in case of the local density approximation. Of course, the main advantage of these quantum Monte Carlo calculations lies in the inclusion of many-particle interactions. In sharp contrast to the one-particle approximation of the usual density functional approaches, in the presented study 256 valence electrons have been considered.
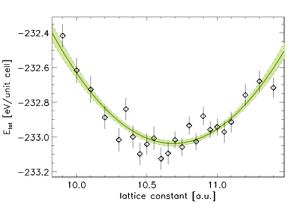 Fig. 1: Total energy vs. lattice constant of GaAs from a VQMC calculation including 256 valence electrons; the curve is a quadratic fit. For that fit the dashed curve gives the confidence interval taking one standard deviation. A larger image is available here.
In the first many-particle calculation of GaAs several ground state properties
have been determined. Fig. 1 shows the total energy as a function of the
lattice constant. The resulting lattice constant is in very good agreement
with the experimental value and better than the results from density
functional calculations. Besides other properties,
the ionicity of the ions and the covalent bond charge
were estimated. In contrast to expectations from rough qualitative arguments, a
surprisingly slight charge accumulations of 0.13 electron per bond appears
on the occupied Ga-As bond .
See also:
|
1996
![]()
 |